Cruithne was discovered on October 10, 1986, by Duncan Waldron on a photographic plate taken with the UK Schmidt Telescope at Siding Spring Observatory, Coonabarabran, Australia. The 1983 apparition (1983 UH) is credited to Giovanni de Sanctis and Richard M. West of the European Southern Observatory in Chile. It was not until 1997 that its unusual orbit was determined by Paul Wiegart and Kimmo Innanen, working at York University in Toronto, and Seppo MIKKOLA, working at the University of Turku in Finland.
The asteroid is named after the Cruithne or Cruthin, the people of early medieval Ireland mentioned in the Annals of Ulster. They are the ancient Pretani, from whom Britain gets its name and are the subject of my first book of that name Cruthin-The Ancient Kindred. In Great Britain, or Alba, they were known as Picts.
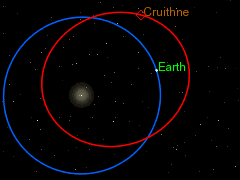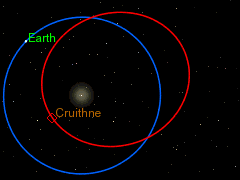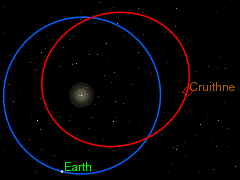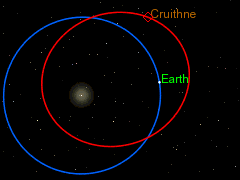
Cruithne is in a normal elliptic orbit around the Sun. Its period of revolution around the Sun, approximately 364 days at present, is almost equal to that of the Earth. Because of this, Cruithne and Earth appear to “follow” each other in their paths around the Sun. This is why Cruithne is sometimes called “Earth’s second moon”. However, it does not orbit the Earth and is not a moon. In 2058, Cruithne will come within 0.09 AU (13.6 million kilometres) of Mars. Due to a high orbital eccentricity, Cruithne’s distance from the Sun and orbital speed vary a lot more than the Earth’s, so from the Earth’s point of view Cruithne actually follows a kidney bean-shaped horseshoe orbit ahead of the Earth, taking slightly less than one year to complete a circuit of the “bean”. Because it takes slightly less than a year, the Earth “falls behind” the bean a little more each year, and so from our point of view, the circuit is not quite closed, but rather like a spiral loop that moves slowly away from the Earth.
After many years, the Earth will have fallen so far behind that Cruithne will then actually be “catching up” on the Earth from “behind”. When it eventually does catch up, Cruithne will make a series of annual close approaches to the Earth; this will alter Cruithne’s orbit by a little over half a million kilometres—while Earth’s orbit is altered by about 1.3 centimetres (0.51 in)—so that its period of revolution around the Sun will then become slightly more than a year. The kidney bean will then start to migrate away from the Earth again in the opposite direction – instead of the Earth “falling behind” the bean, the Earth is “pulling away from” the bean. The next such series of close approaches will be centred on the year 2292 – in July of that year, Cruithne will approach Earth to about 12,500,000 kilometres (7,800,000 mi).
After 380 to 390 years or so, the kidney-bean-shaped orbit approaches Earth again from the other side, and the Earth, once more, alters the orbit of Cruithne so that its period of revolution around the Sun is again slightly less than a year (this last happened with a series of close approaches centred on 1902, and will next happen with a series centered on 2676). The pattern then repeats itself.
Cruithne plays a major role in Steven Baxter’s novel Manifold: Time, which was nominated for the Arthur C. Clarke science fiction award in 2000.